When planning to import goods, deciding on the mode of transport is crucial. In 2026, with fluctuating energy costs and evolving regulations, this choice is not just a simple logistics question; it is a strategic lever for your business performance.
Organizing Air or Sea Freight to Switzerland presents specific challenges. Located in the heart of Europe but outside the European Union/EEA, Switzerland has its own unique customs borders and procedures.
The classic dilemma importers face is: should you prioritize the speed of the sky or the economy of the sea? This choice directly impacts:
- The delivery time
- The global cost (transport + customs)
- The safety of the merchandise
- The fluidity of Swiss customs clearance
To help you navigate these options, here is the ultimate guide to making the right choice based on your goods, constraints, and business objectives.
Air Freight to Switzerland: The Fastest Solution
This mode of transport is synonymous with agility. It offers frequent and rapid arrivals via the main Swiss hubs, particularly via the cargo facilities at Geneva Airport (GVA) or Zurich (ZRH).
Average Transit Times:
- China → Switzerland: 3 to 5 days
- USA → Switzerland: 2 to 4 days
Ideal If:
- Your goods are urgent (product launch, stockout prevention).
- You are transporting high-value products (electronics, luxury watches, pharmaceuticals).
- Your volumes are small or have low bulk.
The Trap to Avoid: Air freight rates depend on volumetric weight as much as actual weight. A light but very bulky shipment (like uncompressed textiles) can cost a fortune by air.

Sea Freight to Switzerland: The Optimized Cost
Maritime transport remains the backbone of international trade for large volumes. Since Switzerland has no direct sea access, routing is generally done via a major European port like the Port of Rotterdam or Antwerp. The goods are then transported by train or truck (combined transport) to the Swiss border.
Average Transit Times:
- Asia → Switzerland: 30 to 40 days door-to-door (including pre- and post-carriage).
Ideal If:
- You are transporting heavy and dense merchandise.
- You have large volumes (pallets, Full Container Load FCL).
- You have no immediate urgency and want to reduce costs to the maximum.
Express Comparison: Air vs. Sea
| Criterion | Air Freight | Sea Freight |
| Transit Time | 3–5 days (Fast) | 30–40 days (Slow) |
| Cost | High | Very Economical |
| Price Calculation | Volumetric Weight (Taxable) | Volume (CBM) / Container |
| Risk | Very Low (Fewer handling points) | Medium (Multiple handling points) |
| Ideal For | Urgent, High Value, Fragile | Heavy, Bulky, Stock |
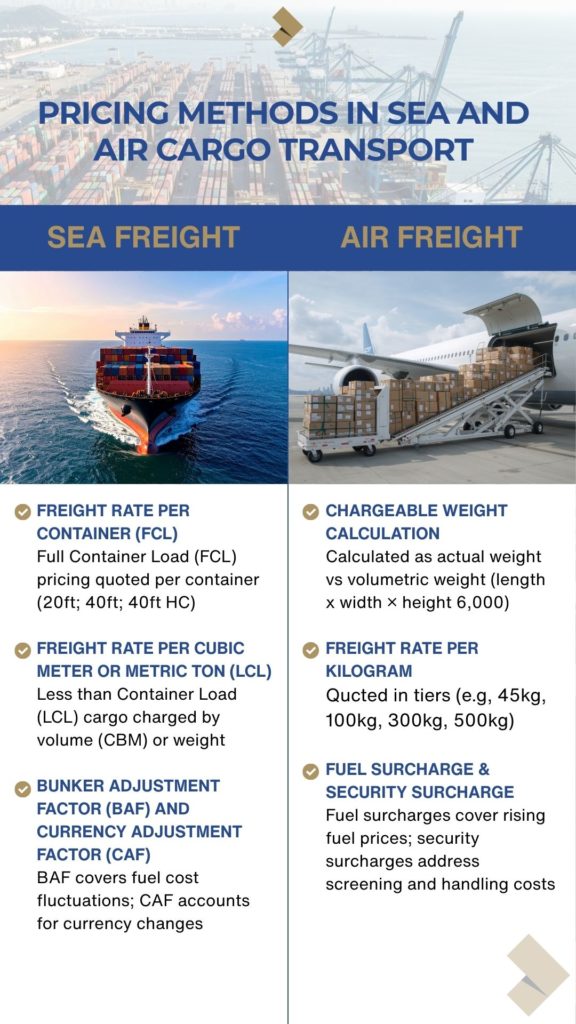
Understanding the Cost Structure
To avoid unpleasant surprises on your final invoice, it is essential to understand how prices are built.
1. In Air Freight: The price depends on weight, dimensions, and the departure airport. Be aware of fuel and security surcharges which can vary monthly.
2. In Sea Freight: The price depends on volume in cubic meters (CBM) or the type of container (20′ or 40′). Don’t forget to include Terminal Handling Charges (THC) and the final road transport to Switzerland.
Expert Tip: The choice of Incoterm (EXW, FOB, DAP) is decisive. It defines who pays for the main transport and insurance. A wrong Incoterm can double your actual costs.
The Decisive Criterion: The Value / Volume Ratio
This is the secret seasoned importers use to decide:
- High Value + Small Volume (e.g., Watches, Electronic Components) → Air. The transport cost represents a small percentage of the goods’ value. Speed secures your cash flow.
- Low Value + Large Volume (e.g., Furniture, Basic Textiles) → Sea. Air freight would be too expensive relative to the product margin.
🇨🇭 Specifics: Swiss Customs Clearance
Unlike a delivery between France and Germany, importing into Switzerland requires formal customs clearance. A documentation error can block your goods at the border, generating storage fees (which are particularly high in airport zones).
Ensure you master the specific Swiss import customs procedures or use a certified customs broker for a seamless operation.
Conclusion: Anticipate to Win
In 2026, there is no absolute “best” transport. A winning logistics strategy often involves combining both: using sea freight for base stock (more economical) and air freight for urgent restocking (more responsive).
The choice of Air or Sea Freight to Switzerland should not be made at random. It deserves a precise analysis of your deadlines and margins.
FAQ – Importing into Switzerland by Air or Sea
How much does transport from China to Switzerland cost? This depends entirely on the chosen mode, volume, and volumetric weight. Air is fast but costly; sea is slow but very economical per CBM. There is no single price.
Is sea freight possible for Switzerland? Yes, absolutely. Goods arrive at a major European port (like Rotterdam or Antwerp) and are then transported by truck or train under customs bond to Switzerland for final clearance.
Which is fastest for Switzerland? Air freight is undoubtedly the fastest, with average transit times of 3 to 5 days from Asia, compared to several weeks for sea freight.
How to calculate volumetric weight? The standard formula is: Length (cm) × Width (cm) × Height (cm) / 6000. This calculation determines the air freight rate if the volumetric weight is higher than the actual weight.
What is the best choice for starting imports into Switzerland? It all depends on your goods and business model. The value/volume ratio is often the determining criterion to start.
Need a free logistics audit?
At Agence Fret Cargo, we analyze your merchandise to guide you toward the most profitable solution. Contact us today to secure your imports.









